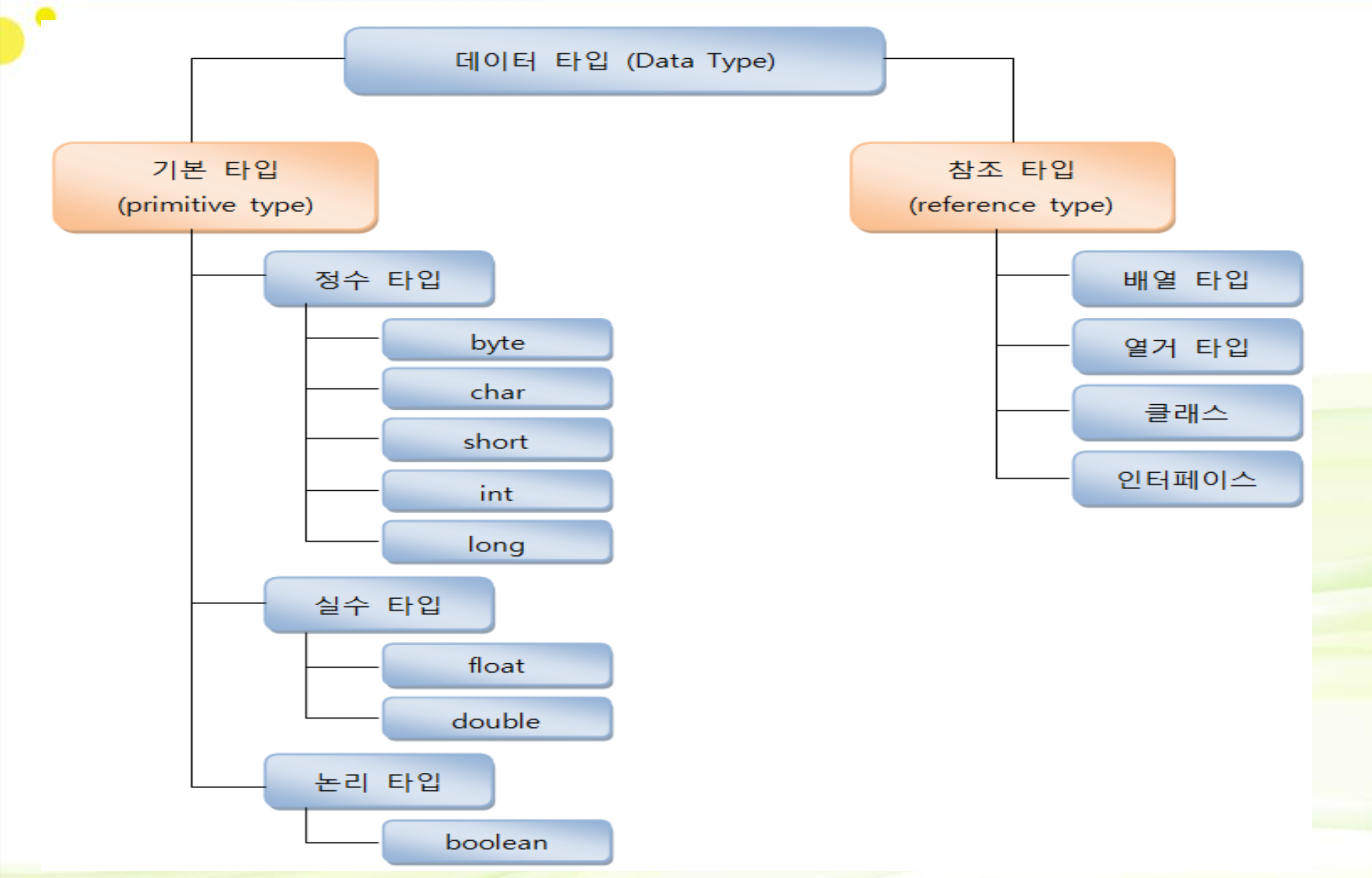
참조 타입 (Reference type)
변수의 메모리 사용
– 기본타입변수–실제값을변수안에저장
– 참조타입변수–주소를통해객체참조
변수의 값이 같은지 다른지 비교
– 기본 타입: byte, char, short, int, long, float, double, boolean • 의미:변수의값이같은지다른지조사
– 참조타입:배열,열거,클래스,인터페이스
• 의미:동일한객체를참조하는지다른객체를참조하는지조사
null(널)
– 변수가참조하는객체가없을경우초기값으로사용가능 – 참조타입의변수에만저장가능
– null로 초기화된 참조 변수는 스택 영역 생성
NullPointerException의 의미
– 예외(Exception)
• 사용자의잘못된조작이나잘못된코딩으로인해발생하는프로그램오류
– NullPointerException
• 참조변수가null값을가지고있을때
– 객체의 필드나 메소드를 사용하려고 했을 때 발생
Array (배열)
배열(arry)이란?
- 같은 형의 데이터들을 다수 개 저장할 수 있는 기억장소를 의미 ➢하나의 이름으로 다수 개의 데이터를 사용할 수 있음
- 학생 10명 성적의 평균을 구하는 프로그램을 작성시 많은 변수를 사용 하여 프 로그램을 복잡하게 하여 오류를 발생시킬 수 있다.
Array(배열)
같은 종류의 데이터를 저장하기 위한 자료구조 배열을 객체로 취급배열을 선언할때 배열의 크기를 명시하지 않는다. [ ]는 앞에 오나 뒤에 오나 상관이 없다. 어떤 형으로 사용할 것인가를 정하고 배열변수를 정해준다.
자료형이 동일한 여러 개의 값을 연이어 저장 할 수 있도록 하는 기억 공간의 집합체(모임)
원소(Element)
– 배열에 저장된 각각의 값
인덱스(색인) : index
– 배열의 원소에 접근하기 위한 첨자
– 만일 배열의 이름이 a라면 배열 원소는 a[0], a[1], a[2], ... 로 표시
배열의 선언
int[] arr;배열의 생성
arr = new int[5];
배열의 생성과 선언을 동시에
int[] arr = new int[5];>> 위 코드는 5개의 원소를 저장할 수 있는 배열을 선언하고 생성하는 것이다.
배열요소의 이용
배열요소는 배열변수명과 인덱스 두 가지를 이용한다.
※인덱스란? 배열의 맨 처음부터의 위치이다. 주의할 점은 자바에
서의 인덱스는 0부터 시작한다는 것이다.
배열 변수명[인덱스] Name[0]=3;
배열의 선언과 생성
int[] a = new int[5]배열에 값 대입
int [ ]a ={10, 20, 30, 40, 50};배열의 원소값 출력
for(i=0; i<a.length; i++)
System.out.println( " a[ " + i + " ] = " +a[i]);배열의 개수
a.length
Ex) 배열선언후값대입과원소출력하기
public class Ex01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int []a=new int [5]; int i;
a[0]=50;
a[1]=100; a[2]=150; a[3]=200; a[4]=250;
for(i=0; i<5; i++)
System.out.println( (i+1)+“ th a[" + i + “]=" +a[i]);
} }
배열의 초기화
- 생성된 배열에 처음으로 값을 저장하는 것
Ex) 차원 배열의 초기화
public class Ex02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int []a ={85, 90, 75, 100, 95}; int tot=0;
double avg;
int i;
for(i=0; i<5; i++) tot+=a[i];
avg = (double)tot/5.0; System.out.println(" 총합 = " + tot); System.out.println(" 평균 = " + avg);
} }
1차원 배열
class ArrayEx1{
public static void main(String[ ] args){
char[] ch; //배열선언
ch = new char[ 4] ; / / 배열 생성 //배열초기화
ch[0] = 'J';
ch[1] = 'a';
ch[2] = 'v'; ch[3] = 'a';
/ / 배열 내용 출력
for(int i = 0 ; i < ch.length ; i++) { System.out.println("ch[ "+i+"] :"+ch[ i] );
} }
}
객체형 배열
- 객체형 배열은 객체를 가리킬 수 있는 참조 값(주소)들의 묶음이다. 실제 값이 저장된 기본 자료 형과는 다르게 객체의 reference들의 집합인 것이다.
- 객체형 배열은 집집마다 우편함을 한곳에 모아둔 것과 같다. 각 우편함들은 나 름 대로 특정한 가정이라는 객체(Object)의 주소를 대신하는 것을 의미하며 이 들의 묶음(집합)이 곧 reference배열 또는 객체형 배열이라 한다
Ex) 합계와 평균, 최대값과 최소값 구하기
class ArrayTest3 {
public static void main(String[] arg){
int array[]={76,45,34,89,100,50,90,92};
int sum=0,avg=0,max=0,min=100;
for(int i=0; i<array.length; i++){
sum+=array[i]; if(array[i]>max) max=array[i];
if(array[i]<min) min=array[i];
}
avg=sum/array.length;
System.out.println("합계 = "+sum+" 평균 = "+avg);
System.out.println("최대값은 = "+max+" 최소값은 = "+min);
}
}
Sort (정열)
배열을 오름차순/내림차순으로 정렬
종류 ( 더 많은 종류가 있지만 일단 쉬운 거 두가지)
- Bubble sort
- Selection sort
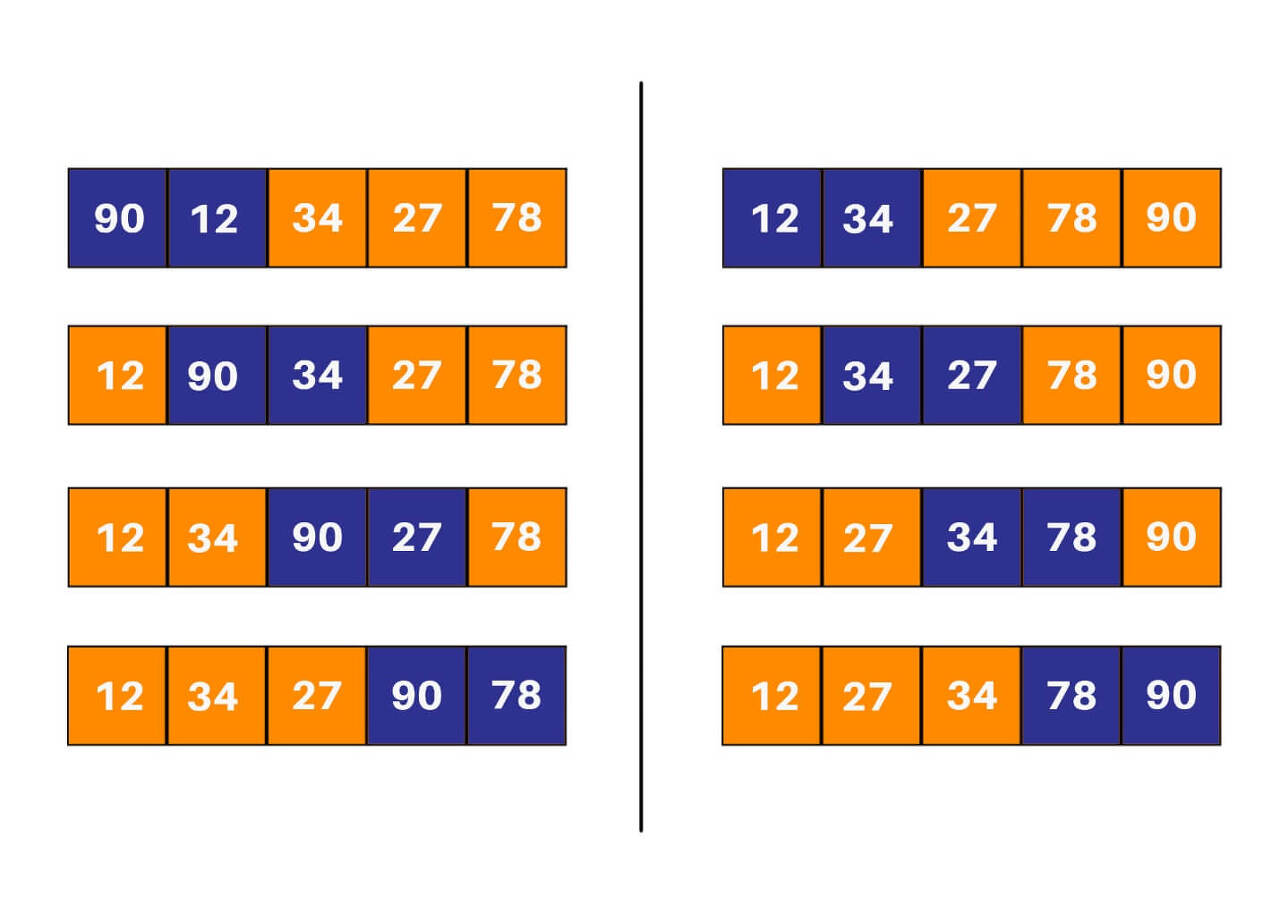
Bubble Sort
logic of bubble sort
class Sort
{
static void bubbleSort(int arr[], int n)
{
if (n == 1) //passes are done
{
return;
}
for (int i=0; i<n-1; i++) //iteration through unsorted elements
{
if (arr[i] > arr[i+1]) //check if the elements are in order
{ //if not, swap them
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[i+1];
arr[i+1] = temp;
}
}
bubbleSort(arr, n-1); //one pass done, proceed to the next
}
void display(int arr[]) //display the array
{
for (int i=0; i<arr.length; ++i)
{
System.out.print(arr[i]+" ");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Sort ob = new Sort();
int arr[] = {6, 4, 5, 12, 2, 11, 9};
bubbleSort(arr, arr.length);
ob.display(arr);
}
}
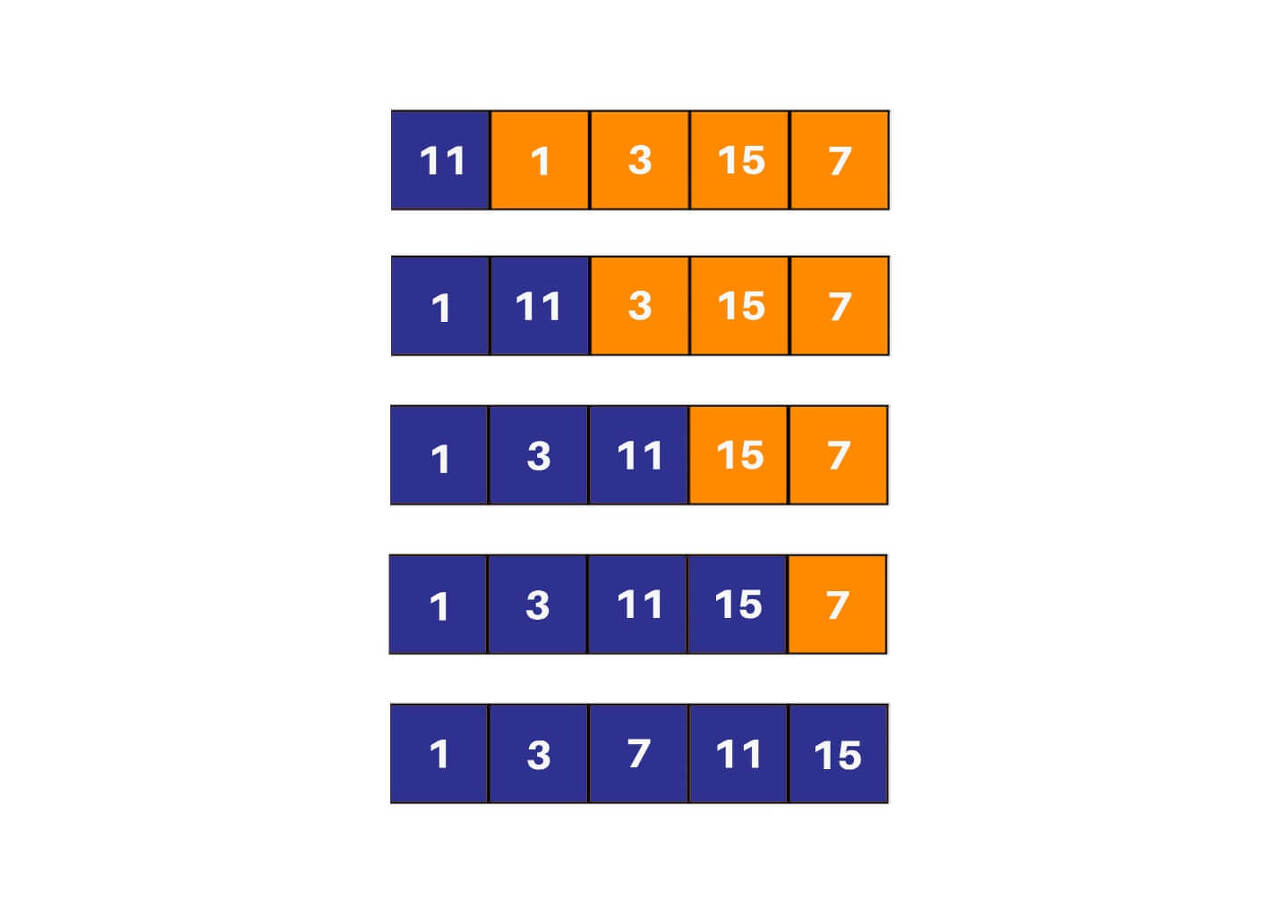
Selection Sort
logic of selection sort
class Sort
{
void selectionSort(int arr[])
{
int pos;
int temp;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++)
{
pos = i;
for (int j = i+1; j < arr.length; j++)
{
if (arr[j] < arr[pos]) //find the index of the minimum element
{
pos = j;
}
}
temp = arr[pos]; //swap the current element with the minimum element
arr[pos] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
}
}
void display(int arr[]) //display the array
{
for (int i=0; i<arr.length; i++)
{
System.out.print(arr[i]+" ");
}
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Sort ob = new Sort();
int arr[] = {64,25,12,22,11};
ob.selectionSort(arr);
ob.display(arr);
}
}
Array 응용문제
Leap Year
package ch04;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Ex04_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int year=0;
do {
System.out.println("Please type a year");
year = sc.nextInt();
if (year==0) break;
// && 가 || 보다 우선 순위다
// 따라서 아래처럼 순서가 바뀌어도 결과가 같다
// year%400==0 || year%4==0 && year%100!=0
if (year%4==0 && year%100!=0 || year%400==0) {
System.out.println("It's a leap year");
} else System.out.println("It's not a leap year");
} while (year!=0);
System.out.println("Bye");
sc.close();
}
}
Lotto (자동/반자동)
package ch04;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Lotto01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int[] lotto = new int[6]; // 1 ~ 45
int temp = 0;
System.out.println("How many number would you like to pick?");
int num = sc.nextInt();
for (int i=0; i<num; i++) {
System.out.println("Type a number");
lotto[i] = sc.nextInt();
//(번호 중복 방지) 앞에 같은 번호가 있는지 확인 하고 있다면 취소
for (int j=i-1; j>=0; j--) { // array 의 앞쪽으로 하나씩 비교해보기
if (lotto[i] == lotto[j]) {
i--; // 현재 인덱스 번호를 취소
break;
}
}
}
for (int i=num; i<lotto.length; i++) {
// 0 ~ 44 => 1 ~ 45
lotto[i] = (int)(Math.random()*45)+1;
// (번호 중복 방지) 앞에 같은 번호가 있는지 확인 하고 있다면 취소
for (int j=i-1; j>=0; j--) { // array 의 앞쪽으로 하나씩 비교해보기
if (lotto[i] == lotto[j]) {
i--; // 현재 인덱스 번호를 취소
break;
}
}
}
for (int i=0; i<lotto.length; i++) {
for (int j=i+1; j<lotto.length; j++) {
if (lotto[i] > lotto[j]) {
temp = lotto[i];
lotto[i] = lotto[j];
lotto[j] = temp;
}
}
}
for (int i=0; i<lotto.length; i++) {
System.out.println(lotto[i]);
}
sc.close();
}
}How many number would you like to pick?
0 // input
3
17
20
27
39
44How many number would you like to pick?
2 //input
Type a number
3 //input
Type a number
11 //input
3
10
11
19
31
35
Array : Sum of each row and column
package ch04;
public class Amount1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String subject = "<Sales Report>"; int len = 54, sum=0;
String[] name = {"fridge", "tv", "vaccum"};
String[] title = {"Prod", "Jan", "Feb","Mar","Apr","Total","Avg"};
int[][] amt = {{250,170,300,780},{170,120,150,220},{450,230,400,250}};
int[] tot = new int[amt[0].length]; // number of columns
System.out.println(subject+"\n");
for (int i=0;i<title.length;i++) {System.out.print(title[i]+"\t");}
System.out.print("\n");
for (int i=0;i<len;i++) {System.out.print("="); if (i==len-1){System.out.print("\n");}}
for (int i=0;i<amt.length;i++) {
System.out.print(name[i]+"\t");
sum=0;
for (int j=0;j<amt[i].length;j++) {
System.out.print(amt[i][j]+"\t");
sum += amt[i][j];
tot[j] += amt[i][j];
}
System.out.print(sum+"\t");
System.out.print(sum/amt[i].length+"\t");
System.out.println();
}
for (int i=0;i<len;i++) {System.out.print("="); if (i==len-1){System.out.print("\n");}}
System.out.print("total\t");
for (int t:tot) {
sum=0;
System.out.print(t+"\t");
sum+=t;
}
System.out.print(sum+"\t"+sum/amt[0].length/amt.length);
}
}result :
<Sales Report>
Prod Jan Feb Mar Apr Total Avg
======================================================
fridge 250 170 300 780 1500 375
tv 170 120 150 220 660 165
vaccum 450 230 400 250 1330 332
======================================================
total 870 520 850 1250 1250 104
array / column / row / sum / average
배열 / 행 / 열 / 합계 / 평균
절차지향 Procedual Programming
'Java Class Notes' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Access Modifier and Encapsulation (접근제어자와 캡슐화) (0) | 2023.02.23 |
|---|---|
| Ex - OOP (0) | 2023.02.23 |
| Method (메소드) (0) | 2023.02.23 |
| Ex - Array (0) | 2023.02.22 |
| 객체 / OPP (Object-Oriented Programming) (1) | 2023.02.21 |